An efficient ruthenium-catalyzed dehydrogenative synthesis of 2,4,6-triaryl-1,3,5-triazines from aryl methanols and amidines†
Abstract
By using [RuCl2(p-Cymene)]2/Cs2CO3 as an efficient catalyst system, the readily available, inexpensive aryl methanols were firstly employed for dehydrogenative synthesis of aryl substituted 1,3,5-triazine derivatives. Due to the inherent stability of alcohols in contrast with aldehydes, our synthetic protocol is adaptable to a broad substrate scope, there is no need for stringent protection during the whole operation process, and it has the potential to prepare valuable products that are currently inaccessible or challenging to prepare using conventional methods. It is a significantly important complement to the conventional synthetic methodologies.
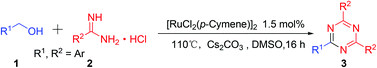

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...