Diverse modifications of the 4-methylphenyl moiety of TAK-779 by late-stage Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling†
Abstract
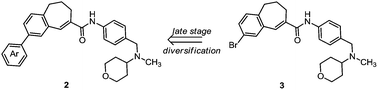
Chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) antagonists provide a new therapeutic approach in the treatment of HIV-1 (AIDS). TAK-779 displays high affinity and selectivity for the CCR5 receptor and serves as a lead compound for the development of further antagonists. In order to increase the oral bioavailability replacement of the quaternary ammonium structure by a tertiary amine and modification of the 4-methylphenyl moiety were envisaged. Herein, a new synthetic strategy for the development of TAK-779 analogs by late stage diversification is reported. The Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reactions allowed various modifications of the central amide building block 3 at the end of the synthesis leading to compounds 2f and 2h with a promising CCR5 binding affinity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...