Novel silica surface charge density mediated control of the optical properties of embedded optically active materials and its application for fiber optic pH sensing at elevated temperatures†
Abstract
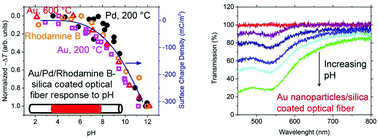
Silica and silica incorporated nanocomposite materials have been extensively studied for a wide range of applications. Here we demonstrate an intriguing optical effect of silica that, depending on the solution pH, amplifies or attenuates the optical absorption of a variety of embedded optically active materials with very distinct properties, such as plasmonic Au nanoparticles, non-plasmonic Pt nanoparticles, and the organic dye rhodamine B (not a pH indicator), coated on an optical fiber. Interestingly, the observed optical response to varying pH appears to follow the surface charge density of the silica matrix for all the three different optically active materials. To the best of our knowledge, this optical effect has not been previously reported and it appears universal in that it is likely that any optically active material can be incorporated into the silica matrix to respond to solution pH or surface charge density variations. A direct application of this effect is for optical pH sensing which has very attractive features that can enable minimally invasive, remote, real time and continuous distributed pH monitoring. Particularly, as demonstrated here, using highly stable metal nanoparticles embedded in an inorganic silica matrix can significantly improve the capability of pH sensing in extremely harsh environments which is of increasing importance for applications in unconventional oil and gas resource recovery, carbon sequestration, water quality monitoring, etc. Our approach opens a pathway towards possible future development of robust optical pH sensors for the most demanding environmental conditions. The newly discovered optical effect of silica also offers the potential for control of the optical properties of optically active materials for a range of other potential applications such as electrochromic devices.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...