Sub-bandgap transverse frequency conversion in semiconductor nano-waveguides
Abstract
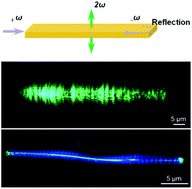
Transverse frequency conversion in the sub-bandgap spectral region is investigated in semiconductor nanowires and nanoribbons using CW lasers with a pump power less than 1 mW. It is found that the properties of the emissions are strongly dependent on the cross-sectional geometries and the surrounding media of nano-waveguides. The polarization is higher in nano-waveguides under single-mode conditions, and the spatial distribution is more tunable in nano-waveguides with higher-order modes involved. Compared with the birefringent approach, transverse frequency conversion shows lower divergence angles, higher polarization, and more tunable spatial distribution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...