The effects of interactions between proline and carbon nanostructures on organocatalysis in the Hajos–Parrish–Eder–Sauer–Wiechert reaction†
Abstract
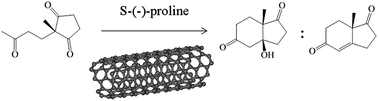
The non-covalent interactions of S-(−)-proline with the surfaces of carbon nanostructures (fullerene, nanotubes and graphite) change the nucleophilic–electrophilic and acid–base properties of the amino acid, thus tuning its activity and selectivity in the organocatalytic Hajos–Parrish–Eder–Sauer–Wiechert (HPESW) reaction. Whilst our spectroscopy and microscopy measurements show no permanent covalent bonding between S-(−)-proline and carbon nanostructures, a systematic investigation of the catalytic activity and selectivity of the organocatalyst in the HPESW reaction demonstrates a clear correlation between the pyramidalisation angle of carbon nanostructures and the catalytic properties of S-(−)-proline. Carbon nanostructures with larger pyramidalisation angles have a stronger interaction with the nitrogen atom lone pair of electrons of the organocatalyst, thereby simultaneously decreasing the nucleophilicity and increasing the acidity of the organocatalyst. These translate into lower conversion rates but higher selectivities towards the dehydrated product of Aldol addition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...