Characterization of tumor-targeting Ag2S quantum dots for cancer imaging and therapy in vivo
Abstract
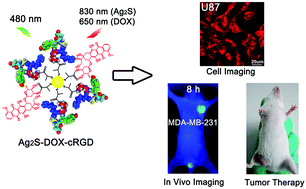
Nanomedicine platforms that have the potential to simultaneously provide the function of molecular imaging and therapeutic treatment in one system are beneficial to address the challenges of cancer heterogeneity and adaptive resistance. In this study, Cyclic RGD peptide (cRGD), a less-expensive active tumor targeting tri-peptide, and doxorubicin (DOX), a widely used chemotherapeutic drug, were covalently attached to Ag2S quantum dots (QDs) to form the nano-conjugates Ag2S-DOX-cRGD. The optical characterization of Ag2S-DOX-cRGD manifested the maintenance of QDs fluorescence, which suggested the potential of Ag2S for monitoring intracellular and systemic drug distribution. The low biotoxicity of Ag2S QDs indicated that they are promisingly safe nanoparticles for bio-applications. Furthermore, the selective imaging and favorable tumor inhibition of the nanoconjugates were demonstrated at both cell and animal levels. These results indicated a promising future for the utilization of Ag2S QDs as a kind of multi-functional nano platform to achieve imaging-visible nano-therapeutics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...