Amine-modified hyaluronic acid-functionalized porous silicon nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer tumors†
Abstract
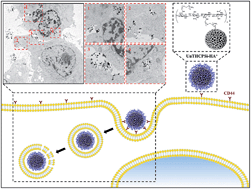
Active targeting of nanoparticles to receptor-overexpressing cancer cells has great potential for enhancing the cellular uptake of nanoparticles and for reducing fast clearance of the nanoparticles from the body. Herein, we present a preparation method of a porous silicon (PSi)-based nanodelivery system for breast cancer targeting, by covalently conjugating a synthesized amide-modified hyaluronic acid (HA+) derived polymer on the surface of undecylenic acid-modified thermally hydrocarbonized PSi (UnTHCPSi) nanoparticles. The resulting UnTHCPSi–HA+ nanoparticles showed relatively small size, reduced polydispersibility, high biocompatibility, improved colloidal and human plasma stability, as well as enhanced cellular interactions and internalization. Moreover, we demonstrated that the enhanced cellular association of UnTHCPSi–HA+ relies on the capability of the conjugated HA+ to bind and consequently target CD44 receptors expressed on the surface of breast cancer cells, thus making the HA+-functionalized UnTHCPSi nanoparticles a suitable and promising nanoplatform for the targeting of CD44-overexpressing breast tumors and for drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...