Analysis of cellular responses of macrophages to zinc ions and zinc oxide nanoparticles: a combined targeted and proteomic approach†
Abstract
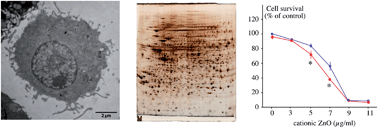
Two different zinc oxide nanoparticles, as well as zinc ions, are used to study the cellular responses of the RAW 264 macrophage cell line. A proteomic screen is used to provide a wide view of the molecular effects of zinc, and the most prominent results are cross-validated by targeted studies. Furthermore, the alteration of important macrophage functions (e.g. phagocytosis) by zinc is also investigated. The intracellular dissolution/uptake of zinc is also studied to further characterize zinc toxicity. Zinc oxide nanoparticles dissolve readily in the cells, leading to high intracellular zinc concentrations, mostly as protein-bound zinc. The proteomic screen reveals a rather weak response in the oxidative stress response pathway, but a strong response both in the central metabolism and in the proteasomal protein degradation pathway. Targeted experiments confirm that carbohydrate catabolism and proteasome are critical determinants of sensitivity to zinc, which also induces DNA damage. Conversely, glutathione levels and phagocytosis appear unaffected at moderately toxic zinc concentrations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...