Self-template construction of hollow Co3O4 microspheres from porous ultrathin nanosheets and efficient noble metal-free water oxidation catalysts†
Abstract
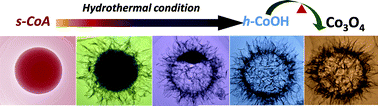
Developing noble metal-free water oxidation catalysts is essential for many energy conversion/storage processes (e.g., water splitting). Herein, we report the facile synthesis of hollow Co3O4 microspheres composed of porous, ultrathin (<5 nm), single-crystal-like nanosheets via a novel “self-template” route. The successful preparation of these hollow Co3O4 nanomaterials includes three main steps: (1) the synthesis of solid cobalt alkoxide microspheres, (2) their subsequent self-template conversion into hollow cobalt hydroxide microspheres composed of ultrathin nanosheets, and finally (3) thermal treatment of hollow cobalt hydroxide microspheres into the hollow Co3O4 material. The as-obtained hollow Co3O4 nanomaterial possesses a high BET surface area (∼180 m2 g−1), and can serve as an active and stable water oxidation catalyst under both electrochemical and photochemical reaction conditions, owing to its unique structural features. In the electrochemical water oxidation, this catalyst affords a current density of 10 mA cm−2 (a value related to practical relevance) at an overpotential of ∼0.40 V. Moreover, with the assistance of a sensitizer [Ru(bpy)3]2+ (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine), this nanomaterial can catalyze water oxidation reactions under visible light irradiation with an O2 evolution rate of ∼12 218 μmol g−1 h−1. Our results suggest that delicate nanostructuring can offer unique advantages for developing efficient water oxidation catalysts.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...