Ullmann-type coupling of brominated tetrathienoanthracene on copper and silver†
Abstract
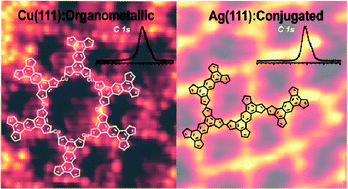
We report the synthesis of extended two-dimensional organic networks on Cu(111), Ag(111), Cu(110), and Ag(110) from thiophene-based molecules. A combination of scanning tunnelling microscopy and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy yields insight into the reaction pathways from single molecules towards the formation of two-dimensional organometallic and polymeric structures via Ullmann reaction dehalogenation and C–C coupling. The thermal stability of the molecular networks is probed by annealing at elevated temperatures of up to 500 °C. On Cu(111) only organometallic structures are formed, while on Ag(111) both organometallic and covalent polymeric networks were found to coexist. The ratio between organometallic and covalent bonds could be controlled by means of the annealing temperature. The thiophene moieties start degrading at 200 °C on the copper surface, whereas on silver the degradation process becomes significant only at 400 °C. Our work reveals how the interplay of a specific surface type and temperature steers the formation of organometallic and polymeric networks and describes how these factors influence the structural integrity of two-dimensional organic networks.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...