Effects of surface roughness of Ag thin films on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of graphene: spatial nonlocality and physisorption strain†
Abstract
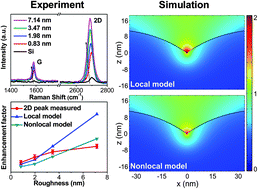
Metallic nanostructures are widely used for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Nanoscale surface corrugation significantly affects the localized plasmon response and the subsequent Raman intensity of the molecules in close proximity to the nanostructures. Experimentally, the surface roughness of metal films can be controlled by adjusting the deposition conditions, and the resulting localized near-field properties can be probed by measuring the Raman spectrum of the conformally coated monolayer graphene. The well-known Raman characteristics of graphene and its atomic-level 2D nature make it an ideal test-bed for SERS measurements on corrugated metal films. In this work, we experimentally and theoretically study the effects of surface roughness of Ag thin films on the SERS of graphene. We find that the nonlocality effect of the metal dielectric response has to be taken into account for more accurate prediction of the SERS enhancement at large surface roughness. Our results also reveal that the effect of physisorption strain should be included to understand the Raman peak shift and spectral broadening. These observations are fundamentally important for understanding the SERS from metallic nanostructures with sub-nanoscale corrugation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...