Bio-inspired formation of functional calcite/metal oxide nanoparticle composites†
Abstract
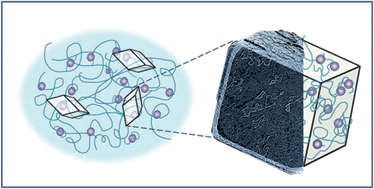
Biominerals are invariably composite materials, where occlusion of organic macromolecules within single crystals can significantly modify their properties. In this article, we take inspiration from this biogenic strategy to generate composite crystals in which magnetite (Fe3O4) and zincite (ZnO) nanoparticles are embedded within a calcite single crystal host, thereby endowing it with new magnetic or optical properties. While growth of crystals in the presence of small molecules, macromolecules and particles can lead to their occlusion within the crystal host, this approach requires particles with specific surface chemistries. Overcoming this limitation, we here precipitate crystals within a nanoparticle-functionalised xyloglucan gel, where gels can also be incorporated within single crystals, according to their rigidity. This method is independent of the nanoparticle surface chemistry and as the gel maintains its overall structure when occluded within the crystal, the nanoparticles are maintained throughout the crystal, preventing, for example, their movement and accumulation at the crystal surface during crystal growth. This methodology is expected to be quite general, and could be used to endow a wide range of crystals with new functionalities.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating the 2017 RSC Prize and Award Winners

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...