Strain sensors based on chromium nanoparticle arrays
Abstract
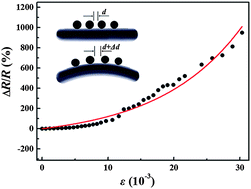
High sensitivity strain sensors have been fabricated by depositing chromium (Cr) nanoparticles between silver interdigital electrodes coated on the substrate of a flexible plastic material like polyethylene terephthalate. A gas phase cluster beam deposition system was used for the preparation of the nanoparticle arrays with a well-defined conductance. We demonstrate that the conductance of the nanoparticle arrays is dominated by the quantum transport between the closely spaced nanoparticles. Compared to the traditional metallic foil or semiconductor strain sensors, this kind of strain sensor demonstrates both a higher gauge factor, which can be as large as the order of 100, and a wider dynamic range, with a workable maximum applied strain beyond 3%.
- This article is part of the themed collection: ChinaNANO

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...