Hydrothermal synthesis of BaZrO3 fine particles controlled in size and shape and fluorescence behavior by europium doping
Abstract
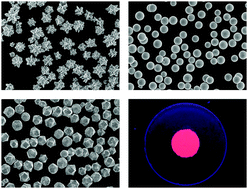
Monodispersed barium zirconate (BaZrO3) fine particles with high crystallinity have been synthesized by hydrothermal reactions using barium hydroxide and a Zr–triethanolamine complex. The particle shape was controlled by changing initial Ba2+ and Zr4+ concentrations, and sphere-, rhombic dodecahedral-, and flower-shaped BaZrO3 fine particles were obtained. On the other hand, the particle mean size of the BaZrO3 microspheres was precisely controlled by the addition of NaOH into the precursor solutions. By Eu-doping, the present BaZrO3 synthesis was also applied to investigate the effect of size and shape on the fluorescence properties of BaZrO3 for its use as a phosphor. The asymmetric ratio of the photoluminescence intensity of the resulting Eu-doped BaZrO3 powders suggested that the particles obtained by the present method had a basically single crystalline structure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...