Facile fabrication of OA-POSS modified near-infrared-emitting CdSeTe alloyed quantum dots and their bioapplications
Abstract
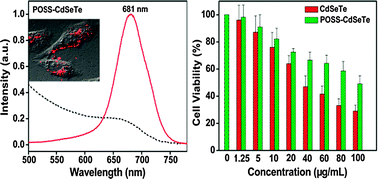
Highly biocompatible near-infrared-emitting CdSeTe alloyed quantum dots (QDs) were fabricated in aqueous medium with octa-aminopropyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (OA-POSS) as the capping agent. By changing the size and composition of CdSeTe alloyed QDs the fluorescence emission peak reached the near infrared (NIR) region (681 nm) with a photoluminescent quantum yield (QY) of 26.4%. POSS–CdSeTe QDs were prepared by conjugating OA-POSS to CdSeTe QDs through condensation reaction utilizing EDC. And the optical properties of CdSeTe QDs were retained with improved biocompatibility. Furthermore, the as-prepared NIR-emitting POSS–CdSeTe alloyed QDs have been successfully applied to SiHa cell imaging, which demonstrates their promising applications in the biomedical field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...