Bile acid amphiphiles with tunable head groups as highly selective antitubercular agents†
Abstract
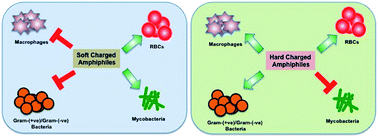
Tuberculosis faces major challenges for its cure due to (a) long treatment period, (b) emergence of drug resistance bacteria, and (c) poor patient compliance. Disrupting the membrane integrity of mycobacteria as a therapeutic strategy has not been explored well as the rigid, waxy, and hydrophobic nature of mycobacterial lipids does not allow binding and penetration of charged amtimicrobial amphiphiles and peptides. Here, we present a new concept that fine-tuning of the charged head group modulates the specificity of amphiphiles against bacterial membranes. We show that hard-charged amphiphiles interact with mycobacterial trehalose dimycolates and penetrate through rigid mycobacterial membranes. In contrast, soft-charged amphiphiles specifically inhibit the growth of both E. coli and S. aureus via electrostatic interactions. These subtle variations between interactions of amphiphiles and bacterial membranes could be explored further to design more specific and potent antimycobacterial agents.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...