Evaluation of functional groups as acetyl-lysine mimetics for BET bromodomain inhibition†
Abstract
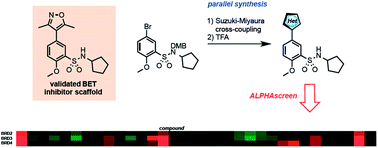
The ability of various functional groups to engage the acetyl-lysine (KAc) binding site within bromo- and extra-terminal domain (BET) protein family members BRD2, BRD3 and BRD4 was evaluated by screening small molecular fragments – coupled to a known arylsulfonamide scaffold – in biochemical inhibition assays. Useful structure activity relationships have been established and novel functional groups that bind to the KAc binding pocket identified. Additional microsomal degradation studies were also undertaken revealing significant differences in metabolic stability between two commonly employed BET inhibitor fragments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...