Recognition of diazirine-modified O-GlcNAc by human O-GlcNAcase†
Abstract
The mammalian O-GlcNAc hydrolase (OGA) removes O-GlcNAc from serine and threonine residues on intracellular glycoproteins. OGA activity is sensitive to N-acyl substitutions to O-GlcNAc, with alkyl diazirine-modified O-GlcNAc (O-GlcNDAz) being completely resistant to removal by OGA. Using homology modeling, we identified OGA residues proximal to the N-acyl position of O-GlcNAc substrate. Mutation of one of these residues, C215, results in mutant enzymes that are able to hydrolytically remove O-GlcNDAz from a model compound. Further, the C215A mutant is capable of removing O-GlcNDAz from a peptide substrate. These results can be used to improve metabolism of O-GlcNAc analogs in cells. In addition, the enzyme specificity studies reported here provide new insight into the active site of OGA, an important drug target.
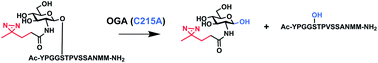

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...