New arginine substituted derivative of poly(allylamine hydrochloride) for heparin reversal†
Abstract
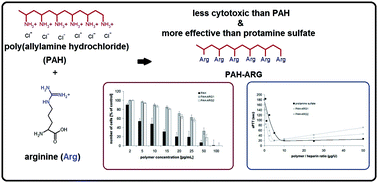
New derivatives of polyallylamine containing arginine moieties (PAH-ARG) were synthesized. The in vitro tests performed in heparinized blood plasma showed that the complexation of heparin by PAH-ARG polymers allowed the reduction of the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) values to the normal level. The dose of PAH-ARG required for complete reversal of aPTT (prolonged by 1 U of heparin) was half of that required for protamine sulfate, the currently used heparin antagonist. The efficacy of these polymers in the neutralization of heparin was confirmed by in vivo tests using a rat model. PAH-ARG polymers were nontoxic to the fibroblast cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...