Necrosulfonamide inhibits necroptosis by selectively targeting the mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein†
Abstract
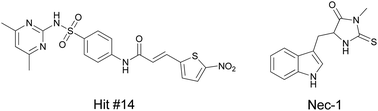
Through high-throughput screening of 200 000 compounds and subsequent structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies we identified necrosulfonamide (NSA) as a potent small molecule inhibitor for necroptosis, induced by a combination of TNF-a, Smac mimetic, and z-VAD-fmk (T/S/Z). Applying a forward chemical genetic approach, we utilized an NSA based chemical probe to further reveal that NSA selectively targeted the Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-like Protein (MLKL) to block the necrosome formation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...