A combined chemometric and quantitative NMR analysis of HIV/AIDS serum discloses metabolic alterations associated with disease status
Abstract
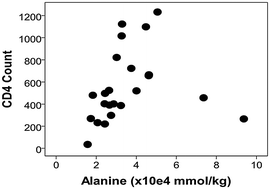
Individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) often suffer from concomitant metabolic complications. Treatment with antiretroviral therapy has also been shown to alter the metabolism of patients. Although chemometric analysis of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of human sera can distinguish normal sera (HIVneg) from HIV-infected sera (HIVpos) and sera from HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy (ART), quantitative analysis of the discriminating metabolites and their relationship to disease status has yet to be determined. The objectives of the study were to analyze NMR spectra of HIVneg, HIVpos, and ART serum samples with a combination of chemometric and quantitative methods and to compare the NMR data with disease status as measured by viral load and CD4 count. High-resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) NMR spectroscopy was performed on HIVneg (N = 10), HIVpos (N = 10), and ART (N = 10) serum samples. Chemometric linear discriminant analysis classified the three groups of spectra with 100% accuracy. Concentrations of 12 metabolites were determined with a semi-parametric metabolite quantification method named high-resolution quantum estimation (HR-QUEST). CD4 count was directly associated with alanine (p = 0.008), and inversely correlated with both glutamine (p = 0.017) and glucose (p = 0.022) concentrations. A multivariate linear model using alanine, glutamine and glucose as covariates demonstrated an association with CD4 count (p = 0.038). The combined chemometric and quantitative analysis of the data disclosed previously unknown associations between specific metabolites and disease status. The observed associations with CD4 count are consistent with metabolic disorders that are commonly seen in HIV-infected patients.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...