An integrated metabonomic approach to studying metabolic profiles in rat models with insulin resistance induced by high fructose
Abstract
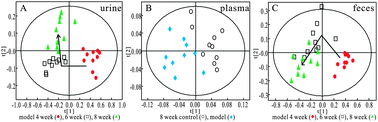
Insulin resistance (IR) is a common risk factor for the development of metabolic diseases, and has gradually become a hot issue for research. It was reported that excessive feeding with high fructose induced insulin resistance in both humans and rats. The aim of this study was to investigate the progression of IR and identify potential biomarkers in urine, plasma and fecal extracts of high fructose-fed rats using a 1H NMR-based metabonomics approach. The biochemical analysis was also performed. The levels of pyruvate and lactate in the plasma of the IR model rats were reduced significantly, and the levels of citrate and α-ketoglutaric acid (α-KG) in their urine, and the levels of succinate in their feces also decreased, suggesting perturbation of energy metabolism. Decreased levels of taurine in urine and fecal extracts during the whole experiment, together with increased levels of creatine/creatinine in urine, revealed liver and kidney injuries. Decreased levels of choline-containing metabolites in urine and increased levels of betaine in urine and plasma demonstrated altered transmethylation. Changes in hippurate, acetate, propionate and n-butyrate levels suggested disturbance of the intestinal flora in the IR rats. This study indicated that 1H NMR-based metabonomics can provide biochemical information on the progression of IR and offers a non-invasive means for the discovery of potential biomarkers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...