Microfluidic generation of chitosan/CpG oligodeoxynucleotide nanoparticles with enhanced cellular uptake and immunostimulatory properties
Abstract
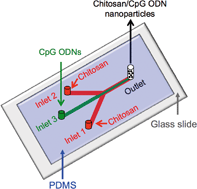
Chitosan/cytosine-phosphodiester-guanine oligodeoxynucleotide (CpG ODN) nanoparticles as potential immunostimulatory adjuvants were synthesized by the conventional bulk mixing (BM) method and a novel microfluidic (MF) method. Their size and size distribution, CpG ODN loading efficiency, surface charge, biocompatibility, cellular uptake, and immunostimulatory response were investigated. In the BM method, nanoparticles were synthesized by vortexing a mixture of chitosan solution and CpG ODN2006x3-PD solution. In the MF method, the nanoparticles were synthesized by rapidly mixing a chitosan solution and CpG ODN solution in a poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic device. Our results indicated that particle size and size distribution, CpG ODN loading efficiency, and surface charge could be easily adjusted by using the tuning preparation method and controlling the flow ratio of fluid rates in the different microfluidic channels. Compared with the BM method, the MF method yielded a decrease in particle size and size range, an increase in CpG ODN loading efficiency, and a decrease in surface charge. After the particles were exposed to 293XL-hTLR9 cells, a water-soluble tetrazolium salt assay indicated that the BM and MF-processed nanoparticles had no significant toxicity and were biocompatible. An immunochemical assay indicated that both types of nanoparticles entered 293XL-hTLR9 cells and were located in the endolysosomes. The MF-processed nanoparticles showed much higher cellular uptake efficiency. After the particles were exposed to peripheral blood mononuclear cells, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay quantitatively indicated that both types of nanoparticles stimulated the production of interleukin-6 and the MF-processed nanoparticles showed a much stronger immunostimulatory response. These results indicate that the MF method can be used to synthesize nanoparticles with a controllable size and size range for enhancing the biological activity of DNA and other biomolecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...