An automated integrated platform for rapid and sensitive multiplexed protein profiling using human saliva samples†
Abstract
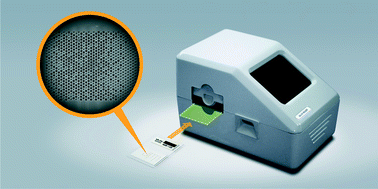
During the last decade, saliva has emerged as a potentially ideal diagnostic biofluid for noninvasive testing. In this paper, we present an automated, integrated platform useable by minimally trained personnel in the field for the diagnosis of respiratory diseases using human saliva as a sample specimen. In this platform, a saliva sample is loaded onto a disposable microfluidic chip containing all the necessary reagents and components required for saliva analysis. The chip is then inserted into the automated analyzer, the SDReader, where multiple potential protein biomarkers for respiratory diseases are measured simultaneously using a microsphere-based array via fluorescence sandwich immunoassays. The results are read optically, and the images are analyzed by a custom-designed algorithm. The fully automated assay requires as little as 10 μL of saliva sample, and the results are reported in 70 min. The performance of the platform was characterized by testing protein standard solutions, and the results were comparable to those from the 3.5 h lab bench assay that we have previously reported. The device was also deployed in two clinical environments where 273 human saliva samples collected from different subjects were successfully tested, demonstrating the device's potential to assist clinicians with the diagnosis of respiratory diseases by providing timely protein biomarker profiling information. This platform, which combines noninvasive sample collection and fully automated analysis, can also be utilized in point-of-care diagnostics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...