Micro-sublimation separation of boron in rock samples for isotopic measurement by MC-ICPMS
Abstract
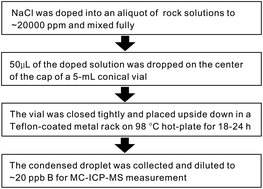
The technique of micro-sublimation for boron (B) separation in silicates has been evaluated carefully. Nine international standards (rock powder) comprising eight felsic to mafic igneous rocks and one clay were dissolved in acids using the HF + mannitol method. These rock solutions were then doped with concentrated NaCl solution and subjected to B micro-sublimation processes. The condensed droplets of micro-sublimation were examined for matrix elements, B recovery, and used for high precision isotopic measurements by MC-ICPMS. These experimental results confirm that the micro-sublimation technique can be used to isolate B in digested silicate solutions efficiently with very low blank and excellent recovery. These new isotopic values in rock standards are in good agreement with literature reports. The inseparable matrix after micro-sublimation suggests a small difference of 0% to −0.8‰ for most silicates in B isotopic measurement using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. This NaCl doping + micro-sublimation technique is readily applicable for B isotopic measurements of silicate rocks containing medium to high B levels (e.g., >5 ppm). This study presents a novel NaCl doping modified micro-sublimation procedure for B isolation in digested silicates. This protocol enjoys low B blank, and is a less labor intensive and simpler procedure compared with traditional ion exchange purification. It can be used to facilitate B isotopic measurements for silicates and promote geochemical applications in environmental aqueous solutions and rocks.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...