Comparative studies of oral administration of marine collagen peptides from Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) pre- and post-acute ethanol intoxication in female Sprague-Dawley rats
Abstract
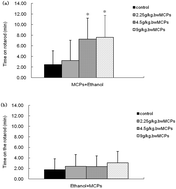
The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of an oral administration of marine collagen peptides (MCPs) pre- and post-acute ethanol intoxication in female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. MCPs were orally administered to rats at doses of 0 g per kg bw, 2.25 g per kg bw, 4.5 g per kg bw and 9.0 g per kg bw, prior to or after the oral administration of ethanol. Thirty minutes after ethanol treatment, the effect of MCPs on motor incoordination and hypnosis induced by ethanol were investigated using a screen test, fixed speed rotarod test (5 g per kg bw ethanol) and loss of righting reflex (7 g per kg bw ethanol). In addition, the blood ethanol concentrations at 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes after ethanol administration (5 g per kg bw ethanol) were measured. The results of the screen test and fixed speed rotarod test suggested that treatment with MCPs at 4.5 g per kg bw and 9.0 g per kg bw prior to ethanol could attenuate ethanol-induced loss of motor coordination. Moreover, MCP administered both pre- and post-ethanol treatment had significant potency to alleviate the acute ethanol induced hypnotic states in the loss of righting reflex test. At 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes after ethanol ingestion at 5 g per kg bw, the blood ethanol concentration (BEC) of control rats significantly increased compared with that in the 4.5 g per kg bw and 9.0 g per kg bw MCP pre-treated groups. However, post-treatment with MCPs did not exert a significant inhibitory effect on the BEC of the post-treated groups until 120 minutes after ethanol administration. Therefore, the anti-inebriation effect of MCPs was verified in SD rats with the possible mechanisms related to inhibiting ethanol absorption and facilitating ethanol metabolism. Moreover, the efficiency was better when MCPs were administered prior to ethanol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...