Glucosinolates from pak choi and broccoli induce enzymes and inhibit inflammation and colon cancer differently†
Abstract
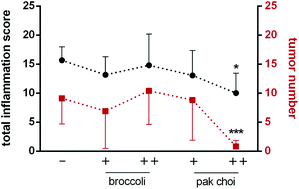
High consumption of Brassica vegetables is considered to prevent especially colon carcinogenesis. The content and pattern of glucosinolates (GSLs) can highly vary among different Brassica vegetables and may, thus, affect the outcome of Brassica intervention studies. Therefore, we aimed to feed mice with diets containing plant materials of the Brassica vegetables broccoli and pak choi. Further enrichment of the diets by adding GSL extracts allowed us to analyze the impact of different amounts (GSL-poor versus GSL-rich) and different patterns (broccoli versus pak choi) of GSLs on inflammation and tumor development in a model of inflammation-triggered colon carcinogenesis (AOM/DSS model). Serum albumin adducts were analyzed to confirm the up-take and bioactivation of GSLs after feeding the Brassica diets for four weeks. In agreement with their high glucoraphanin content, broccoli diets induced the formation of sulforaphane–lysine adducts. Levels of 1-methoxyindolyl-3-methyl-histidine adducts derived from neoglucobrassicin were the highest in the GSL-rich pak choi group. In the colon, the GSL-rich broccoli and the GSL-rich pak choi diet up-regulated the expression of different sets of typical Nrf2 target genes like Nqo1, Gstm1, Srxn1, and GPx2. GSL-rich pak choi induced the AhR target gene Cyp1a1 but did not affect Ugt1a1 expression. Both colitis and tumor number were drastically reduced after feeding the GSL-rich pak choi diet while the other three diets had no effect. GSLs can act anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogenic but both effects depend on the specific amount and pattern of GSLs within a vegetable. Thus, a high Brassica consumption cannot be generally considered to be cancer-preventive.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...