One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous ZnxCd1−xS/reduced graphene oxide hybrid material and its enhanced photocatalytic activity†
Abstract
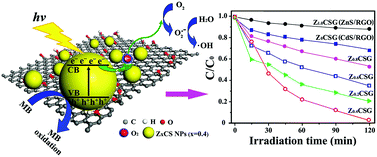
We successfully synthesized mesoporous ZnxCd1−xS/reduced graphene oxide (ZxCSG) hybrid materials as photocatalysts using a facile one-pot hydrothermal reaction, in which graphene oxide (GO) was easily reduced (RGO), and simultaneously ZnxCd1−xS (ZxCS) nanoparticles (NPs) with a mesoporous structure were uniformly dispersed on the RGO sheets. By well tuning the band gap from 3.42 to 2.21 eV by changing the molar ratio of Zn/Cd (or Zn content), ZxCSG with an optimal zinc content has been found to have a significant absorption in the visible light (VL) region. In addition, under VL irradiation (λ > 420 nm), ZxCSG also showed zinc content-dependent photocatalytic efficiencies for the degradation of methylene blue (MB). Our findings are that, among ZxCSG, Z0.4CSG displayed not only a superior photodegradation efficiency of MB (98%), but also good removal efficiency of total organic carbon (TOC) (67%). Furthermore, Z0.4CSG had a high photocatalytic stability, and could be used repeatedly. The enhanced photocatalytic activity for Z0.4CSG could be attributed to a synergistic effect between mesoporous ZxCS NPs and RGO, including the optimal band gap and the moderate conduction band position for ZxCS (compared to CdS), efficient separation and transfer ability of photogenerated electron/hole pairs in the presence of RGO sheets, and relatively high surface area for both mesoporous ZxCS NPs and RGO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...