Synthesis, structure, and peculiar green emission of NaBaBO3:Ce3+ phosphors
Abstract
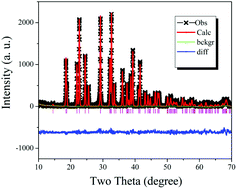
Polycrystalline samples of Ce3+-doped NaBaBO3 (0.5–15 mol%) were prepared by the solid-phase synthesis. The phase formation was confirmed by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) measurements and structural refinement. The photoluminescence excitation and emission spectra and decay curves were measured. The absolute luminescence quantum efficiency (QE) and the activation energy (ΔE) were reported. Under the excitation of near-UV light, Ce3+-doped NaBaBO3 presents a green-emission band centred at 505 nm from the allowed inter-configurational 4f–5d transition. The maximum absolute QE of NaBaBO3:Ce3+ was measured to be 58% excited with 395 nm light at 300 K. The thermal stability of the green luminescence was evaluated by the luminescence decays as a function of temperature. The phosphor shows an excellent thermal stability on temperature quenching effects. Compared with the reported Ce3+-doped alkali metal and alkaline earth orthoborates with the general formula MNBO3 with only blue luminescence, the peculiarity of NaBaBO3:Ce3+ is the green emission and a high doping concentration in the lattices. The results were discussed on the relationship between the structure and the luminescence properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...