Structural and spectroscopic properties of Yb3+-doped MgAl2O4 nanocrystalline spinel
Abstract
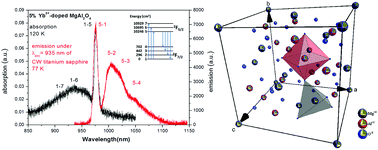
Magnesium spinel (MgAl2O4) powders doped with Yb3+ ions have been synthesized by a sol–gel method and heat-treated in the range of 700–1000 °C for 3 h. XRD patterns indicated that the powders have a cubic structure with high crystallite dispersion. Nanoparticles in the range of 10–30 nm are obtained as a function of the dopant concentration and sintering temperature. The main Yb3+ zero-phonon line is located at 976 nm. The spectroscopic properties of the Yb3+ ions are characterized by broad absorption spectroscopy and emission spectroscopy. Even at low temperature, the spectra reveal a strong distorted spinel lattice due to the high inversion rate between Mg2+ tetrahedral sites and Al3+ octahedral sites. The substitution of Mg2+ ions by Yb3+ ions favors the creation of Yb3+ ion pairs which are observed in the cooperative luminescence spectra at around 500 nm. The luminescence decays are influenced by both the Yb3+ content, the energy transfer between ions and by the presence of pairs and aggregates. Detailed analysis of the observed structural and spectroscopic measurements has been described in this manuscript.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...