MnOx-modified ZnAl-LDOs as high-performance adsorbent for the removal of methyl orange†
Abstract
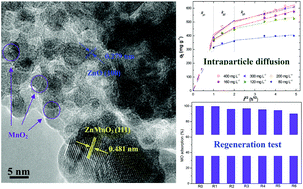
MnOx modified ZnAl layered double oxides (M-LDO) nanocomposites were prepared through an intercalation/reduction/calcination process. The morphology and crystal structure of M-LDO were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis methods. The results confirmed that the manganese oxide nanoparticles were well distributed on the LDO support. Methyl orange (MO) was chosen as a common water-soluble azo dye probe to evaluate the adsorption performance of M-LDO. The effects of MO initial concentration, agitation time, and temperature on MO adsorption were investigated. It was found that adsorption equilibrium data were best represented by the Langmuir and Redlich–Peterson isotherms and the maximum adsorption capacity was 617.28 mg g−1 obtained from the Langmuir isotherm, which was much larger than some reported adsorbents. Besides, the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic in nature and followed a pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The mechanism of the adsorption process was elaborated by an intraparticle diffusion model. Moreover, the regeneration test of M-LDO was carried out and it showed that the used M-LDO was feasible for at least five times. In principle, this adsorbent with a high adsorption capacity and great reutilization performance could be a very promising adsorbent for wastewater treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...