Catalysis and molecular magnetism of dinuclear iron(iii) complexes with N-(2-pyridylmethyl)-iminodiethanol/-ate†
Abstract
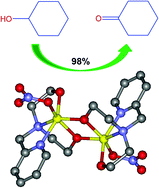
The reaction of N-(2-pyridylmethyl)iminodiethanol (H2pmide) and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O in MeOH led to the formation of a dimeric iron(III) complex, [(Hpmide)Fe(NO3)]2(NO3)2·2CH3OH (1). Its anion-exchanged form, [(pmide)Fe(N3)]2 (2), was prepared by the reaction of 1 and NaN3 in MeOH, during which the Hpmide ligand of 1 was also deprotonated. These compounds were investigated by single crystal X-ray diffraction and magnetochemistry. In complex 1, one iron(III) ion was bonded with a mono-deprotonated Hpmide ligand and a nitrate ion. The two iron(III) ions within the dinuclear unit were connected by two ethoxy groups with an inversion center. In 2, one iron(III) ion was coordinated with a deprotonated pmide ligand and an azide ion. The Fe(pmide)(N3) unit was related by symmetry through an inversion center. Both 1 and 2 efficiently catalyzed the oxidation of a variety of alcohols under mild conditions. The oxidation mechanism was proposed to involve an FeIV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O intermediate as the major reactive species and an FeV
O intermediate as the major reactive species and an FeV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O intermediate as a minor oxidant. Evidence for this proposal was derived from reactivity and Hammett studies, KIE (kH/kD) values, and the use of MPPH (2-methyl-1-phenylprop-2-yl hydroperoxide) as a mechanistic probe. Both compounds had significant antiferromagnetic interactions between the iron(III) ions via the oxygen atoms. 1 showed a strong antiferromagnetic interaction within the Fe(III) dimer, while 2 had a weak antiferromagnetic coupling within the Fe(III) dimer.
O intermediate as a minor oxidant. Evidence for this proposal was derived from reactivity and Hammett studies, KIE (kH/kD) values, and the use of MPPH (2-methyl-1-phenylprop-2-yl hydroperoxide) as a mechanistic probe. Both compounds had significant antiferromagnetic interactions between the iron(III) ions via the oxygen atoms. 1 showed a strong antiferromagnetic interaction within the Fe(III) dimer, while 2 had a weak antiferromagnetic coupling within the Fe(III) dimer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...