Visible light induced photocatalytic activity of sulfur doped hollow TiO2 nanoparticles, synthesized via a novel route†
Abstract
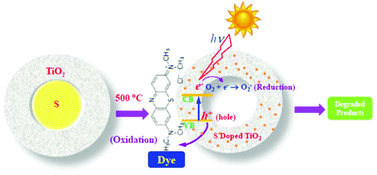
Water pollution by organic pollutants has been a growing global problem in recent years, for which there is a great demand of efficient technologies for wastewater treatment. Remediation of water by photocatalytic oxidation has several advantages over adsorption or any other conventional techniques. This study reports a easy synthesis technique of a sulfur doped hollow TiO2 nanocatalyst for photo degradation of organic dye under solar light. The hollow doped TiO2 nano catalyst has significantly high specific surface area (318.11 m2 g−1) and low band gap (2.5 eV) compared to that of solid particles (130.94 m2 g−1 and 3.2 eV respectively), as a result it acts as an efficient photocatalyst under solar light. The methylene blue dye degradation ability of this catalyst is shown to be 98.6% compared to that of standard Degussa P25 (30%) as reported before. Additionally, the catalyst is also able to degrade 71% methylene blue dye during fifth times recycling without any further treatment because of its high surface area. So our sulfur doped hollow TiO2 nanoparticles can be used as a potential photocatalyst for environmental remediation applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...