Bimetallic ruthenium complexes bridged by divinylphenylene bearing oligo(ethylene glycol)methylether: synthesis, (spectro)electrochemistry and the lithium cation effect†
Abstract
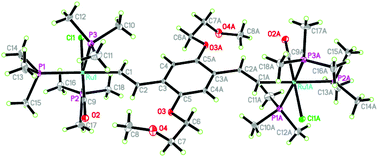
A series of 1,4-disubstituted ruthenium–vinyl complexes, (E,E)-[{(PMe3)3(CO)ClRu}2(μ-HC![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–Ar–CH
CH–Ar–CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH)], in which the 1,4-diethenylphenylene bridge bears two oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether side chains at different positions (2,5- and 2,3-positions), were prepared. The respective products were characterized by elemental analyses and NMR spectroscopy. The structures of complexes 1b and 1e were established by X-ray crystallography. The electronic properties of the complexes were investigated by cyclic voltammetry, and IR and UV-vis/NIR spectroscopies. Electrochemical studies showed that the 2,5-substituents better stabilized the mixed-valence states; the electrochemical behavior was greatly affected by lithium cations, especially complex 1g with 2,3-substituents, which was further supported by IR and UV-vis/NIR spectra changes. Spectroelectrochemical studies showed that the redox chemistry was dominated by the non-innocent character of the bridging fragment.
CH)], in which the 1,4-diethenylphenylene bridge bears two oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether side chains at different positions (2,5- and 2,3-positions), were prepared. The respective products were characterized by elemental analyses and NMR spectroscopy. The structures of complexes 1b and 1e were established by X-ray crystallography. The electronic properties of the complexes were investigated by cyclic voltammetry, and IR and UV-vis/NIR spectroscopies. Electrochemical studies showed that the 2,5-substituents better stabilized the mixed-valence states; the electrochemical behavior was greatly affected by lithium cations, especially complex 1g with 2,3-substituents, which was further supported by IR and UV-vis/NIR spectra changes. Spectroelectrochemical studies showed that the redox chemistry was dominated by the non-innocent character of the bridging fragment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...