High current density electrodeposition of silver from silver-containing liquid metal salts with pyridine-N-oxide ligands†
Abstract
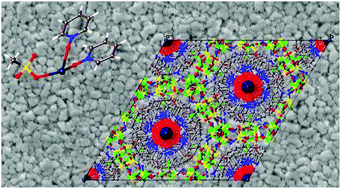
New cationic silver-containing ionic liquids were synthesized and used as non-aqueous electrolytes for the electrodeposition of silver layers. In the liquid state of these ionic liquids, a silver (I) cation is coordinated by pyridine-N-oxide (py-O) ligands in a 1 : 3 metal-to-ligand ratio, although in some cases a different stoichiometry of the silver center crystallized out. As anions, bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (Tf2N), trifluoromethanesulfonate (OTf), methanesulfonate (OMs) and nitrate were used, yielding compounds with the formulae [Ag(py-O)3][Tf2N], [Ag(py-O)3][OTf], [Ag(py-O)3][OMs] and [Ag(py-O)3][NO3], respectively. The compounds were characterized by CHN analysis, FTIR, NMR, DSC, TGA and the electrodeposition of silver was investigated by cyclic voltammetry, linear potential scans, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX). With the exception of [Ag(py-O)3][Tf2N], which melts at 108 °C, all the silver(I) compounds have a melting point below 80 °C and were tested as electrolytes for silver electrodeposition. Interestingly, very high current densities were observed at a potential of −0.5 V vs. Ag/Ag+ for the compounds with fluorine-free anions, i.e. [Ag(py-O)3][NO3] (current density of −10 A dm−2) and [Ag(py-O)3][OMs] (−6.5 A dm−2). The maximum current density of the compound with the fluorinated anion trifluoromethanesulfonate, [Ag(py-O)3][OTf], was much lower: −2.5 A dm−2 at −0.5 V vs. Ag/Ag+. Addition of an excess of ligand to [Ag(py-O)3][OTf] resulted in the formation of the room-temperature ionic liquid [Ag(py-O)6][OTf]. A current density of −5 A dm−2 was observed at −0.5 V vs. Ag/Ag+ for this low viscous silver salt. The crystal structures of several silver complexes could be determined by X-ray diffraction, and it was found that several of them had a stoichiometry different from the 1 : 3 metal-to-ligand ratio used in their synthesis. This indicates that the compounds form crystals with a composition different from that of the molten state. The electrochemical properties were measured in the liquid state, where the metal-to-ligand ratio was 1 : 3. Single crystal X-ray diffraction measurements showed that silver(I) is six coordinate in [Ag(py-O)3][Tf2N] and [Ag(py-O)3][OTf], while it is five coordinate in the other complexes. In [Ag3(py-O)8][OTf]3, there are two different coordination environments for silver ions: six coordinate central silver ions and five coordinate for the outer silver ions. In some of the silver(I) complexes, silver–silver interactions were observed in the solid state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...