Electronic tuning of nitric oxide release from manganese nitrosyl complexes by visible light irradiation: enhancement of nitric oxide release efficiency by the nitro-substituted quinoline ligand†
Abstract
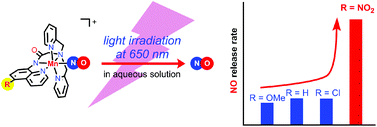
Manganese nitrosyl {MnNO}6 complexes of general formula [Mn(dpaqR)(NO)]ClO4 (1R), where dpaqR denotes a series of pentadentate monoamido ligands, 2-[N,N-bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)]-amino-N′-quinolin-8-yl-acetamido with R = OMe, H, Cl and NO2 at the 5-position of the quinoline moiety, were prepared. The derivatives 1R were characterized by 1H NMR, IR and UV–vis spectrometry as well as by single-crystal X-ray crystallography. The N–O bond and the amido C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O bond stretching frequencies, as well as the redox potentials of 1R derivatives, substantially varied depending on the nature of the substituent group R on the quinoline ring, indicating that the π back-bonding from Mn to NO groups becomes weak as the substituent group R becomes more electron withdrawing. The nitro-substituted derivative 1NO2 is unique among the series; the tail of its absorption bands extends to the NIR region (up to 700 nm), and the apparent NO releasing rate from 1NO2 by light irradiation at 650 nm was ca. 4-fold higher than the other derivatives.
O bond stretching frequencies, as well as the redox potentials of 1R derivatives, substantially varied depending on the nature of the substituent group R on the quinoline ring, indicating that the π back-bonding from Mn to NO groups becomes weak as the substituent group R becomes more electron withdrawing. The nitro-substituted derivative 1NO2 is unique among the series; the tail of its absorption bands extends to the NIR region (up to 700 nm), and the apparent NO releasing rate from 1NO2 by light irradiation at 650 nm was ca. 4-fold higher than the other derivatives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...