Implications of coverage-dependent O adsorption for catalytic NO oxidation on the late transition metals†
Abstract
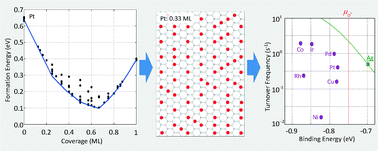
Adsorbate interactions affect both the energies and arrangements of adsorbates on surfaces and consequently influence rates of surface chemical reactions. Here we examine these effects for a rate-limiting O2 dissociation model of catalytic NO oxidation on the late transition metals. We report periodic density functional theory calculations of atomic oxygen adsorption on the (0001) facets of Ru, Os, and Co, and the (111) facets of Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, and Au and correlate these results using cluster expansion (CE) representations. We use grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations implementing these CE Hamiltonians to determine both the number and energetics of first-nearest-neighbor binding site vacancies available for the dissociative adsorption of O2 at conditions representative of catalytic NO oxidation. We estimate steady-state turnover frequencies and compare results to predictions using non-interacting adsorbates. We show that coverage dependence manifests itself in both the energetics and statistical availability of reaction sites and causes rates to deviate substantially from the coverage-independent limit.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Catalysis in the USA


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...