Mn(ii) acetate: an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst for alcohols†
Abstract
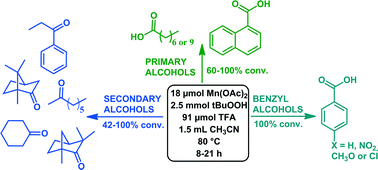
A homogeneous catalytic system consisting of Mn(II) acetate (18 μmol), tert-butylhydroperoxide (2.5 mmol), acetonitrile (1.5 mL) and trifluoroacetic acid (91 μmol) was developed for efficient and selective oxidation of various alcohols (1 mmol). The system yielded good to quantitative conversions (42–100%) of various secondary alcohols, such as 2-octanol, fenchyl alcohol and borneol, to their corresponding ketones. Primary alcohols, for example 1-octanol and differently substituted benzyl alcohols, were mainly converted to their corresponding carboxylic acids. Studies with a selection of hydrocarbons, tertiary amines and a cyclic ether isochroman showed that besides alcohols, other substrates can be oxidised as well.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...