Pt-free tandem molecular photoelectrochemical cells for water splitting driven by visible light
Abstract
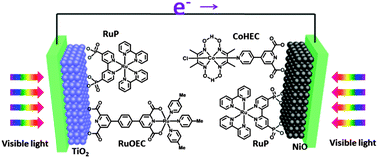
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) cells using molecular catalysts to split water into hydrogen and oxygen have been investigated intensively during the past years. However, the high-cost of Pt counter electrodes and instability of molecular PEC cells hinder the practical applications. We describe in this article a Pt-free tandem molecular PEC cell, for the first time, employing molecular ruthenium- and cobalt-catalysts with strong dipicolinic acid anchoring groups on the respective photoanode and photocathode for total water splitting. The Pt-free tandem molecular PEC cell showed an effective and steady photocurrent density of ca. 25 μA cm−2 for water splitting driven by visible light without external bias. This study indicates that tandem molecular PEC cells can provide great potential to the Pt-free devices for light driven total water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...