Catalytic modification in dehydrogenation properties of KSiH3†
Abstract
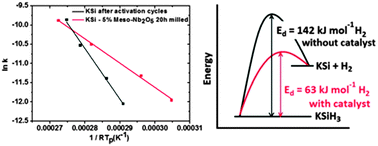
A number of known catalysts, which have been proven to be very effective for several hydrogen species, were studied in order to determine their effects on the hydrogen ab/desorption properties of KSiH3. Among all the catalysts used in this work, mesoporous Nb2O5 is found to be quite effective, with a reduction in activation energy from 142 kJ mol−1 for pristine KSi to 63 kJ mol−1 for mesoporous-Nb2O5-added KSi, thus allowing desorption to start at 100–120 °C. Any disproportionation is not observed in the controlled hydrogenation process. The mechanism for this improvement is also proposed in detail. The kinetic modifications on the ab/desorption properties of KSiH3 provide an alternative to the well-known family of heavy BCC alloys which are capable of working in the same temperature range but with a lower gravimetric hydrogen content, almost half of the KSi system.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...