Spin–flip non-orthogonal configuration interaction: a variational and almost black-box method for describing strongly correlated molecules†
Abstract
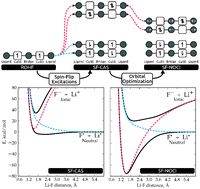
In this paper, we report the development, implementation, and assessment of a novel method for describing strongly correlated systems, spin–flip non-orthogonal configuration interaction (SF-NOCI). The wavefunction is defined to be a linear combination of independently relaxed Slater determinants obtained from all possible spin–flipping excitations within a localized orbital active-space, typically taken to be the singly occupied orbitals of a high-spin ROHF wavefunction. The constrained orbital optimization of each CI basis configuration is defined such that only non-active-space orbitals are allowed to relax (all active space orbitals are fixed). A number of simplifications and benefits arise due to the fact that only a restricted number of orbital rotations are permitted, (1) basis states cannot coalesce during SCF, (2) basis state optimization is better conditioned due to a larger effective HOMO–LUMO gap, (3) smooth potential energy surfaces are easily obtained, (4) the Hamiltonian coupling between two basis states with non-orthogonal orbitals is greatly simplified. To illustrate the advantages over a conventional orthogonal CI expansion, we investigate exchange coupling constants of bimetallic complexes, the avoided crossing of the lowest singlet states during LiF dissociation, and ligand non-innocence in an organometallic complex. These numerical examples indicate that good qualitative agreement can be obtained with SF-NOCI, but dynamical correlation must be included to obtain quantitative accuracy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...