Role of the conformational flexibility of evodiamine in its binding to protein hosts: a comparative spectroscopic and molecular modeling evaluation with rutaecarpine†
Abstract
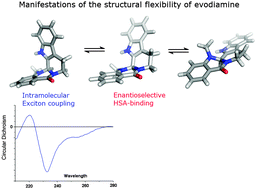
Spectroscopic studies combined with computational analysis indicate the inherent conformational flexibility of the β-carbolin derivative evodiamine (EVD) featured with diverse pharmacological activities. Qualitative evaluation of the circular dichroism (CD) spectra of EVD enantiomers complemented with quantum chemical calculations reveals a chiral exciton signature that can be assigned to the folded, L-shaped conformation of the molecule. Changes of the exciton couplet measured in different solvents and the near-UV CD profile upon binding to human serum albumin (HSA) refer to the structural adaptability of EVD. The enantioselectivity of EVD–HSA interaction is demonstrated showing the binding preference of the (R)-enantiomer. Comparison of experimental and calculated CD spectra of various conformers of EVD as well as the results of molecular docking data suggest that the (R)-antipode is accomodated within the IIA subdomain of HSA in ridge-tile conformation. Rutaecarpine (RTC), the close congener of EVD, forms much tighter association complexes both with HSA and α1-acid glycoprotein. In contrast to EVD, the nearly planar geometry of the indoloquinazoline ring system of RTC allows its stacked dimeric binding to the HSA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...