Complexes formed between DNA and poly(amido amine) dendrimers of different generations – modelling DNA wrapping and penetration
Abstract
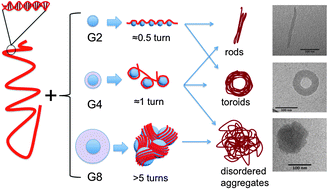
This study deals with the build-up of biomaterials consisting of biopolymers, namely DNA, and soft particles, poly(amido amine) (PAMAM) dendrimers, and how to model their interactions. We adopted and applied an analytical model to provide further insight into the complexation between DNA (4331 bp) and positively charged PAMAM dendrimers of generations 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8, previously studied experimentally. The theoretical models applied describe the DNA as a semiflexible polyelectrolyte that interacts with dendrimers considered as either hard (impenetrable) spheres or as penetrable and soft spheres. We found that the number of DNA turns around one dendrimer, thus forming a complex, increases with the dendrimer size or generation. The DNA penetration required for the complex to become charge neutral depends on dendrimer generation, where lower generation dendrimers require little penetration to give charge neutral complexes. High generation dendrimers display charge inversion for all considered dendrimer sizes and degrees of penetration. Consistent with the morphologies observed experimentally for dendrimer/DNA aggregates, where highly ordered rods and toroids are found for low generation dendrimers, the DNA wraps less than one turn around the dendrimer. Disordered globular structures appear for high generation dendrimers, where the DNA wraps several turns around the dendrimer. Particularly noteworthy is that the dendrimer generation 4 complexes, where the DNA wraps about one turn around the dendrimers, are borderline cases and can form all types of morphologies. The net-charges of the aggregate have been estimated using zeta potential measurements and are discussed within the theoretical framework.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...