π-Cooperativity effect on the base stacking interactions in DNA: is there a novel stabilization factor coupled with base pairing H-bonds?†
Abstract
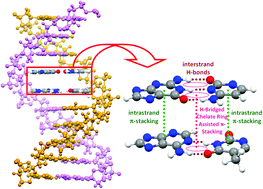
The results from absolutely localized molecular orbital (ALMO)-energy decomposition analysis (EDA) and ALMO-charge transfer analysis (CTA) at M06-2X/cc-pVTZ level reveal that double-proton transfer (DPT) reactions through base pairing H-bonds have nonignorable effects on the stacking energies of dinucleotide steps, which introduces us to a novel stabilization (or destabilization) factor in the DNA duplex. Thus, intra- and inter-strand base stacking interactions are coalesced with each other mediated by H-bridged quasirings between base pairs. Changes in stacking energies of dinucleotide steps depending on the positions of H atoms are due to variations in local aromaticities of individual nucleobases, manifesting π-cooperativity effects. CT analyses show that dispersion forces in dinucleotide steps can lead to radical changes in the redox properties of nucleobases, in particular those of adenine and guanine stacked dimers in a strand. Besides Watson–Crick rules, novel base pairing rules were propounded by considering CT results. According to these, additional base pairing through π-stacks of nucleobases in dinucleotide steps does not cause any intrinsic oxidative damage to the associated nucleobases throughout DPT.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...