Molecules in the mirror: how SERS backgrounds arise from the quantum method of images†
Abstract
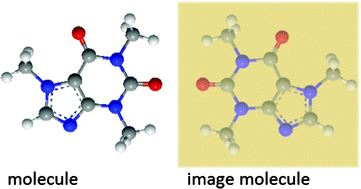
The Raman coupling of light to molecular vibrations is strongly modified when they are placed near a plasmonic metal surface, with the appearance of a strong broad continuum background in addition to the normal surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) peaks. Using a quantum method of images approach, we produce a simple but quantitative explanation of the inevitable presence of the background, due to the resistive damping of the image molecule. This model thus suggests new strategies for enhancing the SERS peak to background ratio.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...