Theoretical study of small sodium–potassium alloy clusters through genetic algorithm and quantum chemical calculations†
Abstract
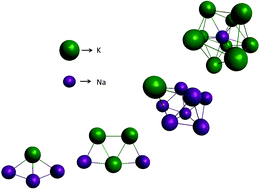
Genetic algorithm is employed to survey an empirical potential energy surface for small NaxKy clusters with x + y ≤ 15, providing initial conditions for electronic structure methods. The minima of such empirical potential are assessed and corrected using high level ab initio methods such as CCSD(T), CR-CCSD(T)-L and MP2, and benchmark results are obtained for specific cases. The results are the first calculations for such small alloy clusters and may serve as a reference for further studies. The validity and choice of a proper functional and basis set for DFT calculations are then explored using the benchmark data, where it was found that the usual DFT approach may fail to provide the correct qualitative result for specific systems. The best general agreement to the benchmark calculations is achieved with def2-TZVPP basis set with SVWN5 functional, although the LANL2DZ basis set (with effective core potential) and SVWN5 functional provided the most cost-effective results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...