The sonochemical approach improves the CuO–ZnO/TiO2 catalyst for WGS reaction†
Abstract
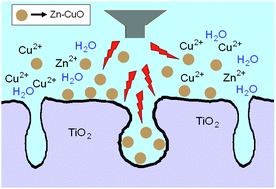
The CuO–ZnO composite was deposited onto two kinds of titania supports, which are synthetic mesoporous TiO2 and commercial TiO2 P25 (Degussa), via the ultrasound assisted precipitation and incipient wetness impregnation (IWI) methods, respectively. The catalysts were tested for WGS reaction in the temperature range of 200–400 °C, and the best catalytic performance was achieved for the sonochemically prepared catalysts supported on the commercial TiO2 P25, which contains well crystallized anatase and rutile phases. Although the synthetic mesoporous TiO2 has a higher surface area, its textural structure is not stable under the reaction conditions, leading to gradual deactivation of the CuO–ZnO/TiO2 catalyst. It is found that the sonochemical preparation offers at least two advantages: (1) generation of mesopores on the catalyst surface and (2) doping of ZnO into the CuO phase. The doping of ZnO, particularly in the case of commercial TiO2 P25, provides high activity and extra stability to the active phase of Cu0. These new findings provide new insights into the design and development of better heterogeneous catalysts for WGS reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...