Solvent dependence of excited-state proton transfer from pyranine-derived photoacids†
Abstract
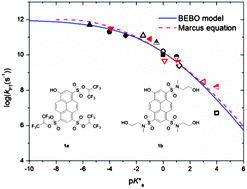
Steady-state and time-resolved techniques were employed to study the excited-state proton-transfer (ESPT) rate of two newly synthesized 8-hydroxy-1,3,6-pyrenetrisulfonate (pyranine, HPTS) derived photoacids in three protic solvents, water, methanol and ethanol. The ESPT rate constant kPT of tris(1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoropropan-2-yl)-8-hydroxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonate, 1a, whose pKa* ∼ −4, in water, methanol and ethanol is 3 × 1011 s−1, 8 × 109 s−1 and 5 × 109 s−1 respectively. (8-Hydroxy-N1,N3,N6-tris(2-hydroxyethyl)-N1,N3,N6-trimethylpyrene-1,3,6 trisulfonamide, 1b) is a weaker acid than 1a but still a strong photoacid with pKa* ∼ −1 and the ESPT rate in water, methanol and ethanol is 7 × 1010 s−1, 4 × 108 s−1 and 2 × 108 s−1. We qualitatively explain our kinetic results by a Marcus-like free-energy correlation which was found to have a general form suitable for describing proton transfer reactions in both the proton-adiabatic and the proton-non-adiabatic limits.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...