Specific anion effects on the pressure dependence of the protein–protein interaction potential
Abstract
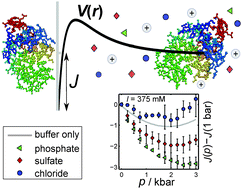
We present a study on ion specific effects on the intermolecular interaction potential V(r) of dense protein solutions under high hydrostatic pressure conditions. Small-angle X-ray scattering in combination with a liquid-state theoretical approach was used to determine the effect of structure breaking/making salt anions (Cl−, SO42−, PO43−) on the intermolecular interaction of lysozyme molecules. It was found that besides the Debye–Hückel charge screening effect, reducing the repulsiveness of the interaction potential V(r) at low salt concentrations, a specific ion effect is observed at high salt concentrations for the multivalent kosmotropic anions, which modulates also the pressure dependence of the protein–protein interaction potential. Whereas sulfate and phosphate strongly influence the pressure dependence of V(r), chloride anions do not. The strong structure-making effect of the multivalent anions, dominating for the triply charged PO43−, renders the solution structure less bulk-water-like at high salt concentrations, which leads to an altered behavior of the pressure dependence of V(r). Hence, the particular structural properties of the salt solutions are able to influence the spatial organization and the intermolecular interactions of the proteins, in particular upon compression. These results are of interest for exploring the combined effects of ionic strength, temperature and pressure on the phase behavior of protein solutions, but may also be of relevance for understanding pressure effects on the hydration behavior of biological matter under extreme environmental conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...