Mechanistic studies of photoinduced intramolecular and intermolecular electron transfer processes in RuPt-centred photo-hydrogen-evolving molecular devices†
Abstract
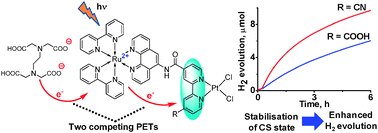
The photoinduced electron transfer properties of two photo-hydrogen-evolving molecular devices (PHEMDs) [(bpy)2Ru(II)(phen-NHCO-bpy-R)Pt(II)Cl2]2+ (i.e., condensation products of [Ru(bpy)2(5-amino-phen)]2+ and (4-carboxy-4′-R-bpy)PtCl2; bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine, phen = 1,10-phenanthroline; RuPt-COOH for R = COOH and RuPt-CN for R = CN) were investigated. RuPt-CN demonstrates higher photocatalytic performance relative to RuPt-COOH arising from a larger driving force for the intramolecular photoinduced electron transfer (PET) associated with a stronger electron-withdrawing effect of R (ΔGPET = −0.43 eV for RuPt-CN and −0.16 eV for RuPt-COOH). This is the first study on PET events using ultrafast spectroscopy. Dramatic enhancement is achieved in the rate of PET in RuPt-CN (1.78 × 1010 s−1) relative to RuPt-COOH (3.1 × 109 s−1). For each system, the presence of three different conformers giving rise to three different PET rates is evidenced, which are also discussed with the DFT results. Formation of a charge-separated (CS) state [(bpy)2Ru(III)(phen-NHCO-bpy−˙-R)Pt(II)Cl2]2+ in the sub-picosecond time regime and recombination in the picosecond time regime are characterized spectrophotometrically. The CS-state formation was found to compete with reductive quenching of the triplet excited state by EDTA whose dianionic form ion-pairs with dicationic RuPt-COOH. Thus, a key intermediate [(bpy)2Ru(II)(phen-NHCO-bpy−˙-R)Pt(II)Cl2]+ (i.e., the one-electron-reduced species) prior to the H2 formation was found to be formed either via reduction of the CS state by EDTA or via formation of [(bpy)2Ru(II)(phen−˙-NHCO-bpy-R)Pt(II)Cl2]+ by reductive quenching of the triplet excited state. More importantly, it is also shown that some of the conformers in solution possess a CS lifetime sufficiently long to drive hydrogen evolution from water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...